What is Zeolite?
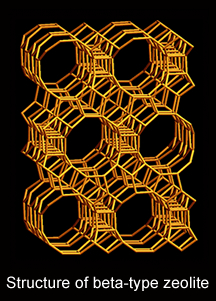
from:
International Zeolite Association (IZA)
http://www.iza-structure.org/databases/
Zeolites are a series of aluminosilicate crystals containing regular molecular-sized open spaces within the structure. The main components of zeolite are silicon (Si), aluminium (Al) and oxygen (O). The basic tetrahedral units (SiO4 and AlO4), are connected three dimensionally to form various zeolite structures. Therefore, the zeolite framework is charged negatively, which is compensated by positive ions. These structural characteristics are the origin of the unique features such as selection of molecules by the size (molecular sieving) and exchange of internal ions with external ones (ion exchange). In addition, by introducing proton by ion exchange, acidity like hydrochloric acid or sulphuric acid can be materialized even though it is a solid.
Beta-type zeolite with a large, three-dimensional pore network can be used widely as catalysts and adsorbents in vehicles’ emission control and the chemical/petrochemical processes.

